Innovative digital watermarking technique developed to enhance image security
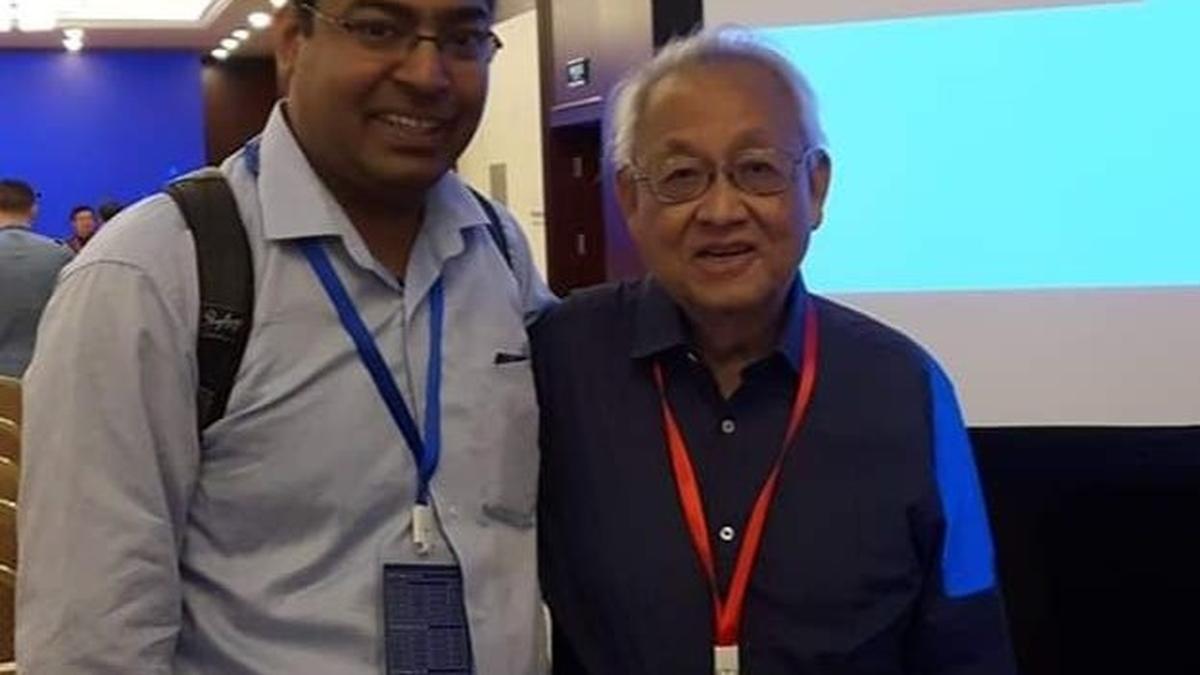


Alex James of Digital University Kerala (left) and Leon Chua of the University of California, Berkeley.
A collaborative study involving Digital University Kerala has introduced an advanced digital watermarking technique that embeds device-specific watermarks into digital images, offering strong protection against machine learning-based attacks.
The model holds promise for applications in intellectual property protection, secure image transmission and IoT device authentication to enhance digital security.
The innovative method uses processing in-memory physical unclonable functions (PUFs) combined with cellular memristor networks (CeNNs). PUFs generate unique digital fingerprints for objects based on their physical properties, making them difficult to replicate under various conditions.
Developed by researchers Alex James (Digital University Kerala), Chithra Reghuvaran (University College Dublin) and Leon Chua (University of California, Berkeley), the technology improves security against counterfeiting and unauthorised copying. The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, highlights the ability of the system to resist advanced machine learning attacks.
Unique
The system works by creating a unique “fingerprint” for each image using the random behaviour of memristors, which are tiny electronic devices. This makes it extremely difficult for anyone to duplicate the watermark, even with sophisticated software.
What sets this method apart from traditional techniques is its energy efficiency. Unlike older methods that rely on separate processors, this technology processes information directly within memory, reducing power consumption and making the watermark even harder to replicate.
The researchers point out the potential applications for this technique are vast. It could revolutionise intellectual property protection by ensuring the authenticity of digital images and preventing content forgery. The system also promises secure image transmission, particularly in sensitive fields like medical imaging, surveillance and military communications. It also provides a robust solution for device authentication in IoT environments, thereby enhancing hardware-level security.
Despite its promising advantages, the researchers acknowledge challenges in verifying watermark integrity when images are compressed, cropped or transformed post-embedding. Future research is expected to explore advanced techniques, such as redundant watermarking and machine learning-based recovery to address these issues.
Published – February 18, 2025 07:07 pm IST